Popular Single-Character Japanese Kanji & Chinese Symbol Wall Scrolls
Here are the single-character words that customers have requested time and again over the last 17 years.
1. Love
6. Wisdom
11. Balance / Peace
14. Inner Peace / Silence / Serenity
Love
愛 universally means love in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, old Korean Hanja, and old Vietnamese.
愛 is one of the most recognized Asian symbols in the West and is often seen on tee shirts, coffee mugs, tattoos, and more.
愛 can also be defined as affection, to be fond of, to like, or to be keen on. It often refers to romantic love, and is found in phrases like, “I love you.” But in Chinese, one can say, “I love that movie” using this character as well.
This can also be a pet name or part of a pet name in the way we say “dear” or “honey” in English.
This can be a girl’s name “Ai” in both Chinese and Japanese.
More about this character:
This may be hard to imagine as a westerner but the strokes at the top of this love character symbolize family & marriage.
![]() The symbol in the middle is a little easier to identify. It is the character for "heart" (it can also mean "mind" or "soul"). I guess you can say that no matter if you are from the East or the West, you must put your heart into your love.
The symbol in the middle is a little easier to identify. It is the character for "heart" (it can also mean "mind" or "soul"). I guess you can say that no matter if you are from the East or the West, you must put your heart into your love.
![]() The strokes at the bottom create a modified character that means "friend" or "friendship."
The strokes at the bottom create a modified character that means "friend" or "friendship."
I suppose you could say that the full meaning of this love character is to love your family, spouse, and friends with all of your heart, since all three elements exist in this character.
See Also: I Love You | Caring | Benevolence | Friendliness | Double Happiness Happy Marriage Wall Scroll
Power / Strength
力 is the simplest form of “power” or “strength.”
In Japanese, it is pronounced “chikara” when used alone, and “ryoku” when used in a sentence (there are also a few other possible pronunciations of this Kanji in Japanese).
In some contexts, this can mean ability, force, physical strength, capability, and influence.
Peace / Harmony
和 is the simplest form of peace and harmony.
和 can also be translated as the peaceful ideas of gentle, mild, kind, and calm. With a more harmonious context, it can be translated as union, together with, on good terms with, or on friendly terms.
Most people would just translate this character as peace and/or harmony. 和 is a very popular character in Asian cultures - you can even call it the “peace symbol” of Asia. In fact, this peace and harmony character was seen repeatedly during the opening ceremony of the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing (a major theme of the games).
In old Chinese poems and literature, you might see this used as a kind of "and." As in two things summed together. As much as you could say, "the sun and moon," you could say "the sun in harmony with the moon."
See Also: Inner Peace | Patience | Simplicity
Happiness / Joyful / Joy
喜 is the Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja for the kind of happiness known in the west as “joy.”
喜 can also be translated as rejoice, enjoyment, delighted, pleased, or “take pleasure in.” Sometimes it can mean “to be fond of” (in a certain context).
If you write two of these happiness/joy characters side by side, you create another character known in English as “double happiness,” which is a symbol associated with weddings and happy marriages.
There is another version of this character that you will find on our website with an additional radical on the left side (exactly same meaning, just an alternate form). The version of happiness shown here is the commonly written form in China, Japan and South Korea (banned in North Korea).
See Also: Contentment | Happiness | Joy
Double Happiness
(Happy wedding and marriage)
囍 is a common gift for Chinese couples getting married or newly married couples.
As we say in the west, “Two heads are better than one” Well, in the east, two “happinesses” are certainly better than one.
Some will suggest this is a symbol of two happinesses coming together. Others see it as a multiplication of happiness because of the union or marriage.
囍 is not really a character that is pronounced very often - it's almost exclusively used in written form. However, if pressed, most Chinese people will pronounce this “shuang xi” (double happy) although literally there are two “xi” characters combined in this calligraphy (but nobody will say “xi xi”).
 If you select this character, I strongly suggest the festive bright red paper for your calligraphy. Part of my suggestion comes from the fact that red is a good luck color in China, and this will add to the sentiment that you wish to convey with this scroll to the happy couple.
If you select this character, I strongly suggest the festive bright red paper for your calligraphy. Part of my suggestion comes from the fact that red is a good luck color in China, and this will add to the sentiment that you wish to convey with this scroll to the happy couple.
Wisdom
智 is the simplest way to write wisdom in Chinese, Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
Being a single character, the wisdom meaning is open to interpretation, and can also mean intellect, knowledge or reason, resourcefulness, or wit.
智 is also one of the five tenets of Confucius.
智 is sometimes included in the Bushido code but is usually not considered part of the seven key concepts of the code.
See our Wisdom in Chinese, Japanese and Korean page for more wisdom-related calligraphy.
See Also: Learn From Wisdom | Confucius
Believe / Faith / Trust
śraddhā
信 can mean to believe, truth, faith, fidelity, sincerity, trust, and confidence in Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji.
This single character is often part of other words with similar meanings.
It is one of the five basic tenets of Confucius.
In Chinese, it sometimes has the secondary meaning of a letter (as in the mail) depending on context but it will not be read that way when seen on a wall scroll.
In the Buddhist context, this is śraddhā (faith through hearing or being taught).
Good Luck / Good Fortune
福 is pronounced “fu” in Chinese.
The character “fu” is posted by virtually all Chinese people on the doors of their homes during the Spring Festival (closely associated with the Chinese New Year).
One tradition from the Zhou Dynasty (beginning in 256 B.C.) holds that putting a fu symbol on your front door will keep the goddess of poverty away.
福 literally means good fortune, prosperity, blessed, blessedness, happiness, and fulfillment.
You'll also see this character in Vietnam (where Chinese characters were the written form until a romanization reform) where it is pronounced Phúc - a word commonly used in Vietnamese names because of its good meaning.
See Also: Lucky
Buddhism / Buddha
佛 is the essence of the Buddha or Buddhism.
Depending on the context, this word and character can be used to refer to the religion and lifestyle of Buddhism, or in some cases, the Buddha himself.
It is interesting to note that this word is separate from all others in the Chinese language. The sound of “fo” has only this meaning. 佛 is in contrast to many sounds in the Chinese language, which can have one of four tones, and more than 20 possible characters and meanings. This language anomaly shows how significantly Buddhism has affected China since ancient times.
More about Buddhism
佛 is also used with the same meaning in Korean Hanja.
It's used in the very religious context of Buddhism in Japan. It should be noted that there are two forms of this Kanji in use in Japan - this is the more formal/ancient version, but it's rarely seen outside of religious artwork and may not be recognized by all Japanese people.
It also acts as a suffix or first syllable for many Buddhist-related words in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
See our Buddhism & Zen page
See Also: Bodhisattva | Enlightenment
Zen / Chan / Meditation
...as in Zen Buddhism
First, let's correct something: The Japanese romanization for this character, “Zen” has penetrated the English language. In English, it's almost always incorrectly used for phrases like “That's so zen.” Nobody says, “That's so meditation” - right? As the title of a sect, this would be like saying, “That's so Baptist!"
禪 by itself just means “meditation.” In that context, it should not be confined to use by any one religion or sect.
Regardless of the dictionary definition, more often than not, this character is associated with Buddhism. And here is one of the main reasons:
Zen is used as the title of a branch of Mahayana Buddhism, which strongly emphasizes meditation practice.
However, it should be noted that Buddhism came from India, and “Chan Buddhism” evolved and developed in medieval China. The Chinese character “Chan” was eventually pronounced as “Zen” in Japanese. Chan Buddhists in China have much in common with Zen Buddhists in Japan.
More about the history of Zen Buddhism here.
Please also note that the Japanese Kanji character for Zen has evolved a little in Japan, and the two boxes (kou) that you see at the top of the right side of the character have been replaced by three dots with tails.
 The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.
The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.![]() There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
Further notes: Zen is just one of seven sects of Buddhism practiced in Japan. The others are 律 Ritsu (or Risshū), 法相 Hossō, 論 Sanron 華嚴 Kegon, 天台 Tendai, and 眞言 Shingon.
Balance / Peace
平 is a single character that means balance in Chinese but it's not too direct or too specific about what kind of balance.
Chinese people often like calligraphy art that is a little vague or mysterious. In this way, you can decide what it means to you, and you'll be right.
平 is also part of a word that means peace in Chinese, Japanese, and old Korean.
Some alternate translations of this single character include: balanced, peaceful, calm, equal, even, level, smooth, or flat.
Note that in Japanese, this just means “level” or “flat” by itself (not the best choice for balance if your audience is Japanese).
Calm / Tranquility
安 is used in a lot of compound words in the CJK world.
Alone, this character has a broad span of possible meanings. These meanings include relaxed, quiet, rested, contented, calm, still, to pacify, peaceful, at peace, soothing, or soothed.
安 and even the pronunciation was borrowed from Chinese and absorbed into both Japanese Kanji and Korean Hanja. In all these languages, this character is pronounced like “an.”
Eternity / Forever
永 is the simplest form of eternity or “always and forever.”
永 can sometimes mean forever, always, perpetual, infinite, or “without end,” depending on context.
Note: Not often seen as a single Kanji in Japanese. Best if your audience is Chinese.
See Also: Forever | Ever Lasting
Inner Peace / Silence / Serenity
靜 is the simplest way to convey the meaning of inner peace and serenity.
靜 is often translated as “serenity.” It can also be used to express the ideas of still, calm, serene, quiet, silent, stillness, not moving, or tranquility.
In the old days, Chinese, Japanese, or Korean people might hang a wall scroll with this character in their reading room to bring about a sense of peace in the room.
![]() While they once used the same character form in Japan, they now use a slightly-simplified version in modern Japan (after WWII). This version is shown to the right, and can be selected for your wall scroll by clicking on that Kanji instead of the button above.
While they once used the same character form in Japan, they now use a slightly-simplified version in modern Japan (after WWII). This version is shown to the right, and can be selected for your wall scroll by clicking on that Kanji instead of the button above.
See Also: Peace
Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
Chi Energy: Essence of Life / Energy Flow
This 氣 energy flow is a fundamental concept of traditional Asian culture.
氣 is romanized as “Qi” or “Chi” in Chinese, “Gi” in Korean, and “Ki” in Japanese.
Chi is believed to be part of everything that exists, as in “life force” or “spiritual energy.” It is most often translated as “energy flow” or literally as “air” or “breath.” Some people will simply translate this as “spirit,” but you must consider the kind of spirit we're talking about. I think this is weighted more toward energy than spirit.
The character itself is a representation of steam (or breath) rising from rice. To clarify, the character for rice looks like this: ![]()
Steam was apparently seen as visual evidence of the release of “life energy” when this concept was first developed. The Qi / Chi / Ki character is still used in compound words to mean steam or vapor.
The etymology of this character is a bit complicated. It's suggested that the first form of this character from bronze script (about 2500 years ago) looked like these samples: 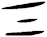
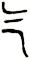
However, it was easy to confuse this with the character for the number three. So the rice radical was added by 221 B.C. (the exact time of this change is debated). This first version with the rice radical looks like this: 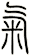
The idea of Qi / Chi / Ki is really a philosophical concept. It's often used to refer to the “flow” of metaphysical energy that sustains living beings. Yet there is much debate that has continued for thousands of years as to whether Qi / Chi / Ki is pure energy or consists partially or fully of matter.
You can also see the character for Qi / Chi / Ki in common compound words such as Tai Chi / Tai Qi, Aikido, Reiki, and Qi Gong / Chi Kung.
In the modern Japanese Kanji, the rice radical has been changed into two strokes that form an X.
![]() The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
More language notes: This is pronounced like “chee” in Mandarin Chinese, and like “key” in Japanese.
This is also the same way to write this in Korean Hanja where it is Romanized as “gi” and pronounced like “gee” but with a real G-sound, not a J-sound.
Though Vietnamese no longer use Chinese characters in their daily language, this character is still widely known in Vietnam.
See Also: Energy | Life Force | Vitality | Life | Birth | Soul
Longevity / Long Life
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Love | 愛 爱 | ai | ài / ai4 / ai | |
| Power Strength | 力 | chikara / ryoku | lì / li4 / li | |
| Peace Harmony | 和 | wa | hé / he2 / he | ho |
| Happiness Joyful Joy | 喜 | ki / yorokobi | xǐ / xi3 / xi | hsi |
| Double Happiness | 囍 喜喜 | xǐ / xi3 / xi | hsi | |
| Wisdom | 智 | chi / tomo | zhì / zhi4 / zhi | chih |
| Believe Faith Trust | 信 | shin | xìn / xin4 / xin | hsin |
| Good Luck Good Fortune | 福 | fuku | fú / fu2 / fu | |
| Buddhism Buddha | 佛 | hotoke | fó / fo2 / fo | |
| Zen Chan Meditation | 禪 禅 | zen | chán / chan2 / chan | ch`an / chan |
| Balance Peace | 平 | hira | píng / ping2 / ping | p`ing / ping |
| Calm Tranquility | 安 | an | ān / an1 / an | |
| Eternity Forever | 永 | ei | yǒng / yong3 / yong | yung |
| Inner Peace Silence Serenity | 靜 静 | shizu / sei | jìng / jing4 / jing | ching |
| Life Energy Spiritual Energy | 氣 气 / 気 | ki | qì / qi4 / qi | ch`i / chi |
| Longevity Long Life | 壽 寿 | ju / kotobuki | shòu / shou4 / shou | |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||



















