Many custom options...
And formats...

Sword and Mind as One in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Sword and Mind as One calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Sword and Mind as One” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Sword and Mind as One” title below...
Switched to secondary search mode due to lack of results using primary.
These secondary results may not be very accurate. Try a different but similar meaning word or phrase for better results. Or...
Look up Sword and Mind as One in my Japanese Kanji & Chinese Character Dictionary(My dictionary is a different system then the calligraphy search you just tried)
If you want a special phrase, word, title, name, or proverb, feel free to contact me, and I will translate your custom calligraphy idea for you.
1. Sword
2. One Day Seems Like 1000 Years
3. Ace / One
4. Beautiful Heart / Beautiful Mind
8. Bodhicitta: Enlightened Mind
10. Body and Mind
11. Body Mind Spirit
12. Buddha Heart / Mind of Buddha
13. Seeing one’s Nature and becoming a Buddha
15. Mark the boat to find the lost sword / Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world
16. Working Together as One / Cooperation
17. Drinking the water of a well: One should never forget who dug it
18. The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet
19. The one who retreats 50 paces mocks the one to retreats 100
22. Words Have Enormous Weight: One Word Worth Nine Caldrons
23. Heijoshin / Presence of Mind
24. Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot
25. Immovable Mind
26. Seeking Mind
27. One Justice Can Overpower 100 Evils
28. The Nature of Enlightenment in One's Mind
30. Kendo / The Way of the Sword
31. Resolute Mind
32. To Know Hardship, One Must Experience It
33. We are not born with knowledge, how does one achieve maturity?
34. Lingering Mind
36. Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark
37. Live By The Sword Die By The Sword
39. Be Master of Mind, Not Mastered by Mind
40. Merciful Heart / The Light from a Buddha Mind
41. Mind Body Spirit
42. Mind Over Matter
43. Energy Sword Body in Concert
45. Mind’s Eye
46. Mind Like Water
47. Morality of Mind
48. No Mind / Mushin
49. No one knows a son better than the father
50. One Direction
52. One Heart / One Mind / Heart and Soul
54. One Love
55. One Mind / Unity
56. One who walks by the river may end up with wet feet
57. One
59. Open Mind
60. An Open Book Benefits Your Mind
62. Patience Brings Peace of Mind
63. Patience Yields Peace of Mind
64. Peace of Mind
65. Peaceful Heart / Peace of Mind / Calm Mind
67. Presence of Mind
68. Prideful Mind / Self-Respecting Heart
70. Purity of Mind
71. One Who Does Not Do Bad Things, Worries Not of Knocks at His Door
72. One who is drenched in rain does not fear drops of dew
73. Sword of Death
77. The Strong One
78. Sword Saint
79. The Chosen One
80. A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One
81. When Three People Gather, One Becomes a Teacher
83. Trust No One / Trust No Man
84. Truth Flashed Through The Mind
85. Tsuki no Kokoro / Mind like the Moon
86. There is one single thread binding my Way together
87. A Wise Man Changes His Mind
88. Work Together with One Mind
89. Work Together with One Heart
90. Solidarity / Working Together as One
Sword
劍 is pronounced “jian” in Chinese. When you say it, imagine that you are making the sound of a sword as it clashes with a metal shield. This might get you closer to the correct pronunciation in Chinese.
I actually wonder if this word came from the metallic ringing sounds of a sword in battle - but such knowledge is lost in history.
The sword is a symbol of a warrior. The one thing that a soldier in ancient China lived and died by. A warrior with his skills and sword proves himself of great value. A warrior who losses his sword instantly becomes worthless.
劍 is an excellent scroll for someone in the military (especially officers of all services - as well as enlisted NCO Marines since they still carry swords even if mainly for ceremonial purposes). Or perhaps someone who practices variations of kung fu or tai chi that involve weapons.
Please note that while this character is understood with the sword meaning in Japanese, you might be looking for the word “katana” which also means sword in Japanese but means “knife” in Chinese.
There are other ways to write sword, and here are a few...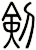
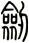
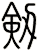
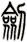
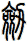
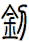


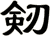

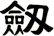
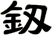



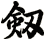
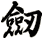
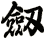
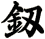






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

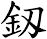
If you are particular about the version you receive, please let me know when you place your order (Note: Special styles are only available from one of our master calligraphers).
Sword
剱 is the modern Japanese way to write sword.
This Kanji character comes from original Chinese. This form would also be understood in Chinese (there are often several ways to write the same character) but I suggest this one only if your audience is Japanese (because they've settled on a slightly different form as the standard in China).
In Japanese, this character also means saber/sabre, blade, bayonet, stinger, and clock hand (clock hands are the “swords” of the clock).
See Also: Katana
One Day Seems Like 1000 Years
一日千秋 is a Japanese and Chinese proverb about missing someone.
一日千秋 is often used to express how hard it is to wait for someone's return or to be away from someone.
Some will translate this as “one day feels like a very long time” or “waiting for someone (something) is hard.”
You might see this romanized as a single word, Ichijitsusenshuu, or as “Ichijitsu Senshuu” from Japanese.
If you break down the characters one-by-one, we get:
一 = one/a
日 = day/sun (can also represent time or date)
千 = 1000/thousand
秋 = autumn/fall
Together, 千秋 can mean “autumn comes thousand times” (or 1000 years). It can also be read as 1000 periods of time.
However, it relays the idea of heartache as you wait for someone you miss.
Ace / One
幺 means one, as used on a dice or in a card game.
Thus, in that context, it means Ace.
幺 can also be the surname “Yao” in both Chinese and Japanese.
Note: Rarely if ever used in Korean.
幺 can sometimes be written these ways: ![]()
![]()
Beautiful Heart / Beautiful Mind
Beautiful Mind
Mind of the Beginner
Shoshin
初心 is often translated in Japanese as “beginner's mind” or “beginner's spirit.”
In Chinese, the dictionary definition is “one's original intention.”
The first character means first, initial, primary, junior, beginning, or basic.
The second character means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
初心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: The state of shoshin is that of a beginners mind. It is a state of awareness that always remains fully conscious, aware, and prepared to see things for the first time. The attitude of shoshin is essential to continued learning.
Best / Number One
Bodhicitta: Enlightened Mind
冒地質多 is a Chinese and Japanese way to write Bodhicitta.
冒地質多 is often translated as “the enlightened mind” or “enlightened heart.”
This title is strictly Buddhist and won't make sense to Chinese or Japanese people who do not have an expansive background in Buddhist terms, concepts, and scripture.
The Bodhi Mind
菩提心 means Bodhi-mind or Bodhi-heart.
This title represents the will to realize supreme enlightenment. The awakening of the Bodhi-mind is of utmost importance in Buddhist training.
Other definitions include the mind for or of bodhi, the awakened, enlightened mind, or having Buddha-nature.
Body and Mind
身心 means “body and mind” or “mental and physical” in Chinese and Japanese.
In the Buddhist context, body and mind encompass the five elements (skandha) of a sentient being.
The body is the physical material (rūpa) of life. The mind embraces the other four skandhas, which are consciousness, perception, action, and knowledge.
Body Mind Spirit
身心霊 means “body mind spirit” in Japanese.
This refers to your physical, mental, and spiritual presence.
This can also be translated as “body heart spirit” as 心 can mean mind or heart.
Note that this is a "word list" and not a proper phrase (with a subject, verb, and object) nor a typical title in Japanese. So it's not too commonly seen in Japan. However, the term 身心霊整合性医療 that refers to holistic medicine is gaining popularity.
Buddha Heart / Mind of Buddha
佛心 means the Buddha's mind, Buddha-heart, or the spiritually enlightened heart/mind.
The Buddha Heart is detached from good and evil and other such constructs. The Buddha Heart has mercy, compassion, and loving-kindness for all sentient life, the good, the wicked, and all in between.
The heart and mind (心) are the same concepts in the ancient Orient, so you can use heart and mind interchangeably in this context.
Seeing one’s Nature and becoming a Buddha
見性成佛 is a universal phrase that suggests that one may see one's nature and accomplish Buddhahood.
見性 suggests penetrating deep inside oneself to see one's “Original finally
Mind.”
成佛 refers to a sentient being who dispenses with illusions and delusions
through ascetic practice, is enlightened to the truth, and becomes a Buddha.
This is used by Mahayana, Chan, and Zen Buddhists in China, Korea, and Japan.
You will also see this with the last character written as 仏 in Japanese. In the religious context, 佛 is commonly used to mean Buddha. If you want the other version, see Kenshō Jōbutsu 見性成仏
Calm and Open Mind
Mark the boat to find the lost sword / Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world
刻舟求劍 is an originally-Chinese proverb that serves as a warning to people that things are always in a state of change.
Thus, you must consider that and not depend on the old ways or a way that may have worked in the past but is no longer valid.
This idiom/proverb comes from the following story:
A man was traveling in a ferry boat across a river. With him, he carried a treasured sword. Along the way, the man became overwhelmed and intoxicated by the beautiful view and accidentally dropped his prized sword into the river. Thinking quickly, he pulled out a knife and marked on the rail of the boat where exactly he had lost his sword.
When the boat arrived on the other side of the river, the man jumped out of the boat and searched for his sword right under where he'd made the mark. Of course, the boat had moved a great distance since he made the mark, and thus, he could not find the sword.
While this man may seem foolhardy, we must take a great lesson from this parable: Circumstances change, so one should use methods to handle the change. In modern China, this is used in business to mean that one should not depend on old business models for a changing market.
This proverb dates back to the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC) of the territory now known as China. It has spread and is somewhat known in Japan and Korea.
Working Together as One / Cooperation
Drinking the water of a well: One should never forget who dug it
This proverb suggests that one should always be grateful to those who helped one succeed.
And remember your ancestors and those that came before you whose sacrifices made your present life better.
Some Chinese will separate the intended meaning from this proverb and translate this as “Don't forget the people who once helped you.” In Modern China, this idiom is virtually never used to refer to an actual well.
Note: This can be pronounced in Korean but it's not a commonly used phrase.
The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet
The one who retreats 50 paces mocks the one to retreats 100
The pot calls the kettle black
五十步笑百步 is a Chinese proverb that means the one who retreats 50 paces mocks the one who retreats 100 paces.
During the Warring States Period of what is now China (475 - 221 B.C.), the King of Wei was in love with war. He often fought with other kingdoms just for spite or fun.
One day, the King of Wei asked the philosopher Mencius, “I love my people, and all say I do the best for them. I move the people from famine-stricken areas to places of plenty and transport grains from rich areas to the poor. Nobody goes hungry in my kingdom, and I treat my people far better than other kings. But why does the population of my kingdom not increase, and why does the population of other kingdoms not decrease?”
Mencius answered, “Since you love war, I will make this example: When going to war, and the drums beat to start the attack, some soldiers flee for their lives in fear. Some run 100 paces in retreat, and others run 50 steps. Then the ones who retreated 50 paces laugh and taunt those who retreated 100 paces, calling them cowards mortally afraid of death. Do you think this is reasonable?
The King of Wei answered, “Of course not! Those who run 50 paces are just as timid as those who run 100 paces.”
Mencius then said, “You are a king who treats his subjects better than other kings treat their people, but you are so fond of war that your people suffer from great losses in battle. Therefore, your population does not grow. While other kings allow their people to starve to death, you send your people to die in war. Is there any difference?”
This famous conversation led to the six-character proverb shown here. It serves as a warning to avoid hypocrisy. It goes hand-in-hand with the western phrase, “The pot calls the kettle black,” or the Biblical phrase, “Before trying to remove a splinter from your neighbor's eye, first remove the plank from your own eye.”
One Good Deed Each Day
一日一善 is a Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja phrase that suggests doing a good deed each day or doing one good turn a day.
It literally reads, “One Day, One Good (Deed).”
Heart / Mind / Spirit
心 would often be translated as “heart.”
However, because it was believed in Chinese culture for thousands of years that your consciousness and thoughts came from the big red organ in the middle of your chest, it also means “mind” or “spirit” and sometimes even “soul.”
In Korean, beyond heart, mind, and spirit, this character can mean moral, nature, mind, affections, intentions, core, and center. In fact, it is used in Chinese to mean “center” as well but only with another character in front of it. For instance, “medical center” or even “shopping center.” Separately and alone, it will not be read with that “center” meaning unless thought of as “the center of your soul.”
Words Have Enormous Weight: One Word Worth Nine Caldrons
一言九鼎 is an ancient Chinese proverb used in modern times to talk of profound or powerful words.
 The literal meaning is “one word [worth] nine [sacred] tripods.” The tripod is a highly-prized three-legged (sometimes four-legged) metal pot or kettle of ancient China. They are often made of bronze, and the Emperor would have large ones gilded in gold. See the image to the right for an example.
The literal meaning is “one word [worth] nine [sacred] tripods.” The tripod is a highly-prized three-legged (sometimes four-legged) metal pot or kettle of ancient China. They are often made of bronze, and the Emperor would have large ones gilded in gold. See the image to the right for an example.
Heijoshin / Presence of Mind
平常心 is the title Heijoshin, as associated with Kendo and Aikido schools of Japanese martial arts.
平常心 is also a word in Japanese that can be translated as “one's self-possession” or “presence of mind.”
In Chinese and Korean, this means “simplicity heart,” “composure,” “calmness,” or a “sense of orderliness.” In Chinese and Korean, this implies that you enjoy what you have, keep your heart in balance, and have no over-blown ambitions.
Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot
Immovable Mind
fudoshin
不動心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet.
Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: An unshakable mind and an immovable spirit is the state of fudoshin. It is courage and stability displayed both mentally and physically. Rather than indicating rigidity and inflexibility, fudoshin describes a condition that is not easily upset by internal thoughts or external forces. It is capable of receiving a strong attack while retaining composure and balance. It receives and yields lightly, grounds to the earth, and reflects aggression back to the source.
Other translations of this title include imperturbability, steadfastness, keeping a cool head in an emergency, or keeping one's calm (during a fight).
The first two Kanji alone mean immobility, firmness, fixed, steadfastness, motionless, and idle.
The last Kanji means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
Together, these three Kanji create a title defined as “immovable mind” within the context of Japanese martial arts. However, in Chinese, it would mean “motionless heart,” and in Korean Hanja, “wafting heart” or “floating heart.”
Seeking Mind
One Justice Can Overpower 100 Evils
一正压百邪 is an ancient Chinese proverb and idiom that means “One Justice Can Overpower a Hundred Evils.”
While this proverb is famous in China, it has been around so long that its origins have been forgotten.
It could be something that Confucius or one of his disciples said, but no one can say for sure.
The Nature of Enlightenment in One's Mind
Life-Saving Sword
活人剣 is a Japanese title for “life-saving sword” or “katsujinken.”
This title suggests that a sword used for killing can also be used for saving or giving life.
See Also: Satsujinken
Kendo / The Way of the Sword
Often associated with Kenjutsu, 剱道/劍道 means “The way of the sword” in Japanese (and Korean with an alternate form of the first character).
This is also the term used for swordsmanship and even fencing in Japanese and Korean, depending on context.
Note: These same characters are also used separately in Chinese, but this exact combination yields a common title in Japanese only (perhaps someone who is really into swords would use this in China).
Note: There is more than one way to write the “sword” character (shown above is the Japanese version - if you want the Korean version, please let me know when you place your order).
Resolute Mind
決定心 means the mind of certainty, resolute mind, imperturbable mind, firm determination, firm resolution, or stable commitment.
In the context of Buddhism, this is the deep resolution needed to attain enlightenment.
If you go to a deeper meaning, this is a condition of settling into the thought that occurs in the process of perception subsequent to the “seeking mind” or “尋求心.”
To Know Hardship, One Must Experience It
不當和尚不知頭冷 is a Chinese proverb that literally translates as: [One who has] not been a monk [does] not know [the feeling of a] cold head.
I need to explain that a Chinese Buddhist monk always has a shaved head, and thus a cold head in winter.
Figuratively, this means: One cannot know the true meaning of hardship until one has experienced it oneself.
This is an idiom in Chinese, so the figurative meaning is what people perceive when they hear or read this phrase. Just as in English, when someone says, "The grass is always greener," one will think about the idea of jealousy, rather than the quality of one’s lawn.
We are not born with knowledge, how does one achieve maturity?
This figuratively means “Without a teacher, how can we learn/mature?”
人非生而知之者熟能無惑 is a philosophic pondering by Han Yu, a Tang Dynasty essayist, and philosopher (618-907 A.D.). This is a Chinese proverb that can be translated as “Knowledge is not innate to man, how can we overcome doubt?” or, “We are not born with knowledge, how does one achieve maturity?.”
This infers that we need the guidance of a teacher if we wish to learn, mature, and become better.
Lingering Mind
Zanshin
First off, 殘心 should only be used in the context of Japanese martial arts. In Chinese, it's a rather sad title (like a broken heart). In Chinese, the first character alone means destroyed, spoiled, ruined, injured, cruel, oppressive, savage, incomplete, or disabled. However, in Japanese, it's remainder, leftover, balance, or lingering.
The second character means heart, mind, soul, or essence in both languages.
殘心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: The spirit of zanshin is the state of the remaining or lingering spirit. It is often described as a sustained and heightened state of awareness and mental follow-through. However, true zanshin is a state of focus or concentration before, during, and after the execution of a technique, where a link or connection between uke and nage is preserved. Zanshin is the state of mind that allows us to stay spiritually connected, not only to a single attacker but to multiple attackers and even an entire context; a space, a time, an event.
![]() In modern Japan (and Simplified Chinese), they use a different version of the first character, as seen to the right. Click on this character to the right instead of the button above if you want this modern Japanese version of lingering mind / zanshin.
In modern Japan (and Simplified Chinese), they use a different version of the first character, as seen to the right. Click on this character to the right instead of the button above if you want this modern Japanese version of lingering mind / zanshin.
Listen with Open Mind
Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark
兼聽則明偏聽則暗 is an ancient Chinese proverb about getting all the information from all sides so that you truly understand a situation.

Wei Zheng
A man named Wei Zheng lived between 580-643 AD. He was a noble and wise historian and minister in the court of the early Tang Dynasty. The emperor once asked him, “What should an emperor do to understand the real-world situation, and what makes an emperor out-of-touch with reality?”
Wei Zheng replied, “Listen to both sides and you will be enlightened; listen to only one side and you will be left in the dark.”
Then Wei Zheng went on to cite examples of leaders in history that were victorious after heeding both sides of the story, and other leaders that met their doom because they believed one-sided stories which often came from flattering lips.
Please note that there is an unwritten rule when the same character appears twice in the same phrase, the calligrapher will alter the appearance so that no two characters are exactly alike in the same piece. This calligraphy has two repeating characters that will be written differently than they appear here.
Live By The Sword Die By The Sword
Matthew 26:52
Loving Heart / One’s Love
戀心 literally means “loving heart.” It can also be translated as “one's love” or “awakening of love.”
戀心 is used exclusively for love between boyfriends and girlfriends or husband and wife.
Breaking down the meaning of each Kanji, the first means love, affection, or tender passion. The second Kanji means heart, mind, or soul (most will read it as the heart).
See Also: Compassion | Love
Be Master of Mind, Not Mastered by Mind
Merciful Heart / The Light from a Buddha Mind
心光 can mean the light from a Buddha's mind or “merciful heart.”
This would especially be the light emanating from Amitābha.
Note that the character 心 can mean mind or heart. 光 means light or brightness - but in this context can suggest a glow of mercy or compassion.
This can also be a Japanese surname that is romanized as Shinkou or Shinko.
Mind Body Spirit
身心靈 is probably the best way to express the idea of “Body, Mind, and Spirit” in Chinese and old Korean Hanja. We are actually using the word “heart” here because, for thousands of years, the heart was thought to be the place where your thoughts, feelings, and emotions came from. We do something similar in the west when we say “warm-hearted” or “I love you with all of my heart.” In this context, heart = mind in Asian language and culture.
The very literal translation of these three characters is “body, heart & spirit,” which could also be interpreted as “body, mind & soul.”
We have arranged these characters in this order because it simply “feels” like the proper order in the Chinese language. Word lists like this are not so common for calligraphy artwork, so we must be careful to put them in the most natural order. It should be noted that this is not a common title in Asia, nor is it considered an actual phrase (as it lacks a clear subject, verb, and object).
![]() In Japanese Kanji, they use an alternate form of the character for soul or spirit. If you want this using the Japanese alternate, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above.
In Japanese Kanji, they use an alternate form of the character for soul or spirit. If you want this using the Japanese alternate, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above.
Japanese disclaimer: This is not a natural phrase/list in Japanese. While not totally-natural in Chinese, this word list is best if your audience is Chinese.
Mind Over Matter
Mind Over Matter
物質性を超越する精神力 means “mind over matter,” in Japanese.
If you get really technical, you get a translation like, “mental strength transcends materiality.”
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Energy Sword Body in Concert
Spirit, Sword & Body as One
气剑体一致 often gets translated as “Mind Sword Body,” or “Spirit, Sword, and Body as One.” But I think these translations don't tell you enough about what this is really saying.
In this context, 気, which is the modern Japanese version of 氣, means spiritual and unseen energy or “life energy.” In some cases, 気 can be translated as spirit, feeling, or nature. If defined as the mind, it's more about the invisible or intangible parts of one's mind (or soul).
剣 is the Japanese version of 劍 meaning sword.
体 is the modern Japanese version of 體 meaning body.
The Kanji 一 means one, and in this case, suggests “all in one.”
The Kanji 到 means to send, deliver, or convey. But together, 一到 suggests all these things in agreement, union cooperation, or in concert.
Note: Arguments exist as to whether this should be romanized as Kikentaiitchi, Kikentaiicchi, or kikentaiichi. Technically, if you drop the last character, you get 気剣体一 and kikentaiichi (ki ken tai ichi), which is also a valid phrase.
Mind Your Own Business
不干己事不张口一问摇头三不知 literally translates as [About] matters [that] don't concern [you], do not open [your] mouth, [and] when questioned, always shake [your] head “No.”
Figuratively, this means: It is best to remain reticent about other people's affairs and to refuse to make any comment on matters that don't concern you.
Mind Your Own Business
余計なお世話 suggests that you do not give unwanted help or advice to someone.
The Japanese characters break down this way:
余計 (yokei) too much, unnecessary, extraneous, abundance, surplus, excess, superfluity.
な (na) connecting article.
お世話 (osewa) help, aid, assistance.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Mind’s Eye
Mind Like Water
Mizu No Kokoro
水の心 is the Japanese Buddhist and martial arts phrase, “Mizu no Kokoro,” which means “mind like water” or “heart of water.”
The phrase is a metaphor describing the pond that clearly reflects its surroundings when calm but whose images are obscured once a pebble is dropped into its waters.
Morality of Mind
The idea of 心德 or “morality of mind” goes along with 行德 or “wu de” (martial morality or virtues of the warrior).
Here, the first character is a representation of your heart or mind.
The second character refers to morality or virtue.
This can also be translated as “morality of heart,” “virtue of heart,” or “virtue of the mind.”
Since ancient times in Asia, the idea of your mind (where your soul resides and your thought originates) has been associated with the heart. Just as in western culture, where we say “it comes from the heart” or “heartfelt emotions,” there is a belief that your heart and mind are one and the same (medical science now begs to differ).
See Also: Morality of Deed | Martial Morality
No Mind / Mushin
In Japanese, 無心 means innocent or without knowledge of good and evil. It literally means “without mind.”
無心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: “No mind, a mind without ego. A mind like a mirror which reflects and dos not judge.” The original term was “mushin no shin,” meaning “mind of no mind.” It is a state of mind without fear, anger, or anxiety. Mushin is often described by the phrase “Mizu no Kokoro,” which means “mind like water.” The phrase is a metaphor describing the pond that clearly reflects its surroundings when calm but whose images are obscured once a pebble is dropped into its waters.
This has a good meaning in conjunction with Chan / Zen Buddhism in Japan. However, out of that context, it means mindlessness or absent-mindedness. To non-Buddhists in China, this is associated with doing something without thinking.
In Korean, this usually means indifference.
Use caution and know your audience before ordering this selection.
More info: Wikipedia: Mushin
No one knows a son better than the father
知子莫若父 can be translated as “No one knows a son better than his father.”
This idiom is based on the idea that after spending many years together, family members know everything about each other. Better than anyone else, a father knows the qualities and shortcomings of his son.
If you are looking for something about “father and son,” this is probably the best selection.
While this is the original proverb (very old), others have been composed about various combinations of mothers, sons, daughters, and fathers. Let me know if you need a custom version.
One Direction
一世代 is a way to write “One Direction” in Chinese, referring to the British-Irish boy band.
They are commonly referred to as “1D” in Japan and China (no Chinese characters for that).
This title does not exactly mean “one direction.” It's closer to “one generation,” “one era,” or “one world.”
One Direction
ワンダイレクション is a way to write “One Direction” in Japanese Katakana, referring to the British-Irish boy band.
They are commonly referred to as “1D” in Japan and China (no Japanese Kanji for that).
This title sounds like “One Direction” using Japanese sounds. Unlike Japanese Kanji words, this does not have any meaning, just pronunciation.
Note: Because this title is entirely Japanese Katakana, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
One Family Under Heaven
天下一家 is a proverb that can also be translated as “The whole world is one family.”
It is used to mean that all humans are related by decree of Heaven.
The first two characters can be translated as “the world,” “the whole country,” “descended from heaven,” “earth under heaven,” “the public,” or “the ruling power.”
The second two characters can mean “one family,” “a household,” “one's folks,” “a house” or “a home.” Usually, this is read as “a family.”
Note: This proverb can be understood in Japanese, though not commonly used.
One Heart / One Mind / Heart and Soul
一心 literally reads as “one heart” in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
Colloquially or figuratively, it means: wholeheartedly; heart and soul; of one mind; wholeheartedness; one's whole heart; with the whole mind or heart; one mind in heart.
I'm not kidding, all of those came right from the dictionary for this one title.
In Buddhism, this can refer to the bhūtatathatā, or the whole of things; the universe as one mind, or a spiritual unity.
In Japanese, this can be the female given name, Hitomi.
One Key Opens One Lock
One Love
One Love
One Mind / Unity
和合 means to blend, unite, or be of one mind.
和合 is usually used as a Buddhist term. It can also be defined as harmony, concord, agreement, unity, union, and harmonize/harmonization.
One who walks by the river may end up with wet feet
常在河邊走哪能不濕鞋 is an old Chinese proverb that is sometimes compared to the English saying “Shit Happens.”
It's a reflection that there are risks in life, and you should not be surprised when things don't go your way.
A secondary translation might be, “When walking by a river, often one cannot avoid wet shoes.”
One
The number one
一 is “one” or “1” in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
People keep searching for “one” but I'm not sure what you want. This would be a strange selection for a wall scroll, so please don't order it. Post a request on our forum if you want a phrase with “one” in it that you can't find on our site.
The “one” character is really simple, it's just one stroke. Two is two strokes and three is three strokes, from four and above, the characters get more complicated.
In some ways, the “one” character is too simple, it could be a stray mark, or added to a banking document. Therefore, the following banking anti-fraud character for “one” has developed over the last 1500 years in China and Japan:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Open and Calm Mind
虛心坦懐 is a Japanese proverb that means “with an open and calm mind,” “with no preconceived notions,” or “without reservations.”
In some contexts, it can mean frank or candid.
If you want to remind yourself to approach each situation with no preconceptions, this is a good title for you. This can also refer to the ideas of being candid, frank, and straightforward.
Open Mind
An Open Book Benefits Your Mind
There are several ways to translate this ancient proverb. Translated literally and directly, it says, “Open roll has/yields benefit.”
To understand that, you must know a few things...
First, Chinese characters and language have deeper meanings that often are not spoken but are understood - especially with ancient texts like this. Example: It's understood that the “benefit” referred to in this proverb is to the reader's mind. Just the last character expresses that whole idea.
Second, Chinese proverbs are supposed to make you think and leave a bit of mystery to figure out.
Third, for this proverb, it should be noted that roll = book. When this proverb came about (about two thousand years ago), books were rolls of bamboo slips strung together. The first bound books like the ones we use today did not come about until about a thousand years after this proverb when they invented paper in China.
開卷有益 is a great gift for a bookworm who loves to read and increase their knowledge. Or for any friend that is or wants to be well-read.
Some other translations of this phrase:
Opening a book is profitable
The benefits of education.
The Original Mind
In Zen Buddhism, 本心 means “original mind” or “original heart,” which refers to one's Buddha-nature present from birth.
This can also be translated as true feelings, real intention, one's own heart, one's right mind, one's senses, one's conscience, or fundamental mind.
Note: 心 can mean heart or mind - thought in ancient Asia to be the same organ.
Patience Brings Peace of Mind
Patience Yields Peace of Mind
Peace of Mind
(five-character version)
內心的寧靜 is the long way to express the idea of “peace of mind” in Chinese.
The first two characters mean heart or “innermost being.”
The middle character is a connecting modifier.
The last two characters mean peace, tranquility, or serenity.
Some may also translate this as “inner peace,” but I like our other inner-peace options for that idea.
This kind of makes sense in Korean but will have an archaic read - even by those who can understand Korean Hanja.
Peace of Mind
和平 is the Chinese order for these two characters, which means peace but can also be translated as amicability, specifically, or mildness. 和平 is often translated as a simple way to say “peace of mind.” This combination is used in Korean Hanja to mean “peace and harmony.”
Alone, the first character means peace and harmony.
The second character means balance when read by itself.
Note: 和平 are often seen in the opposite order in Japanese with the same meaning (You'll sometimes find them in this order in Japan, so either way is OK).
Peaceful Heart / Peace of Mind / Calm Mind
安心 can be defined as relief, peace of mind, feeling at ease, to be relieved, to set one's mind at rest, and easiness.
安心 is a nice word that encompasses great meanings within just two characters. Some of the other meanings include pacifying, settling the mind, and peace of mind. It's also the idea of feeling a sense of security, safety, and confidence in your state of well-being.
This can be used by everyone, but some consider it to be a Buddhist concept (You'll find it in your Zen dictionary).
Note: Can be romanized as Anshin or Anjin in Japanese.
Perfectly Sincere Mind
Presence of Mind
Presence of Mind
Prideful Mind / Self-Respecting Heart
自尊心 is a Japanese and Korean word that means “pride” or “self-respect.”
The first Kanji/Hanja means oneself. The second can mean revered, valuable, precious, noble, or exalted. And the last Kanji/Hanja means heart, mind, and/or spirit.
While these characters make sense and hold the same general meaning in Chinese, this is not a normal Chinese word. This selection should only be used if your audience is Japanese or Korean.
See Also: Respect | Pride | Self-Reliance | Self-Control | Self-Discipline
Proud Of One’s Name
Purity of Mind
心澄淨 is the Buddhist concept of the pure and calm mind. It is believed that once you achieve a meditative state of pure focused thought, the mind becomes clear and calm. Although, others will say this means that achieving a calm mind will allow you to reach pure thought.
From Sanskrit, this is known as citta-prasāda. The concept of citta-prasāda is sometimes defined as “clear heart-mind,” or “the single and definitive aspiration.”
One Who Does Not Do Bad Things, Worries Not of Knocks at His Door
白天不做亏心事夜半敲门不吃惊 literally translates as: [If one does] not do bad things in the daytime, one need not be alarmed at knocks on the door in the middle of the night.
The meaning is something like, “A quiet conscience sleeps in thunder.” Basically, the message is, “don't commit crimes and you won't be jumpy every time the doorbell rings (so don't do anything wrong and your life will have fewer worries and you can sleep at night).”
One who is drenched in rain does not fear drops of dew
Sword of Death
殺人剣 is a Japanese title for “Death Sword,” “Life Taking Sword,” or “satsujinken.”
This is the opposite of katsujinken or the “life-saving sword.” This title is not as commonly used in Japanese but pairs well when hung with katsujinken.
The first two Kanji are a word that translates as homicide, murder or kill (a person). 殺人剣 is specifically to kill a person (as the second character means person or human) as opposed to an animal, etc.
The last Kanji is the Japanese variant of the originally-Chinese character for a sword.
See Also: Katsujinken
Stable - Mind at Peace
安穩 can mean a steady, stable, sedate, and calm mind.
Other translations include “body and mind at rest,” or “peace and comfort.”
Strong Mind Strong Body
Strong Body, Strong Mind
強い体強い心 is a way to write “strong mind, strong body” in Japanese.
Each of the two lines starts with 強い (tsuyoi) which means: strong; powerful; mighty; potent; resistant; resilient; durable; tough; stiff; hard; inflexible.
The body is represented with 体 (the ancient version is 體, romanized as karada), which means: body; build; physique; posture; torso; trunk; health.
Mind is represented with 心 (kokoro), which can mean heart, mind, or soul, depending on context.
強い體強い心 is not a common phrase in Japanese, so it's not the most natural title for calligraphy. In English, you might want to write it, “strong mind, strong body” but, “strong mind, strong body,” is more natural in Japanese.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
The Strong One
Sword Saint
剣聖 can be translated as “Sword Saint,” “God of the Sword,” or “Saint of the Sword.” This is an ancient Japanese title bestowed on a master with the greatest of skills in swordsmanship.
Keep in mind that this is an antiquated term. It will only be understood in the context of martial arts. The pronunciation “kensei” also applies to other words like “constitutional government” and power (these words have different kanji and are completely unrelated).
Notes: This is sometimes Romanized as “kensei,” “ken sei,” and incorrectly as “Kensai.”
Chinese Note: This title is pronounceable in Chinese but seldom, if ever, used in Chinese. Also, the first character is an alternate character form for a sword, currently only used in Japan.
The Chosen One
選ばれし者 is a Japanese title that means “The chosen one” but can also refer to “The select few” or “the chosen ones.”
The last character clarifies that the “one” refers to a person or persons (male or female).
This can also be written 撰ばれし者 or 択ばれし者 with the same pronunciation and meaning. The one shown above is the most common way to write it.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One
千里も一里 is a Japanese proverb that states “A journey of a thousand miles feels like only one mile.” It is understood that in the proverb, this applies when going to see the one you love.
Note that the “mile” or 里 used in this proverb is an old Chinese “li” (pronounced “ri” in Japanese). It's not actually a mile, as the measurement is really closer to 500 meters (it would take 3 of these to get close to a western mile). Still, 1000里 (333 miles) is a long way.
When Three People Gather, One Becomes a Teacher
三人行必有我师 means “when three people meet, one becomes the teacher.”
This famous Chinese philosophy suggests that when people come together, they can always learn from each other.
One person must be the teacher and others learn. And in turn, the others become the teachers of the knowledge they possess.
It is important to remember that we all have something to teach, and we all have something to learn as well.
Time Waits For No One
歳月人を待たず is a Japanese idiom “Saigetsu hito o matazu” which means “Time waits for no one.”
Another way to put it is, “Time and tide stay for no man.”
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Trust No One / Trust No Man
無法信任 is the kind of thing you expect to hear in a spy movie.
“Trust no one, 007!”
The first two characters express the idea of “no way” or “cannot.”
The last two characters mean “trust.”
The characters must go in this order due to Chinese grammar issues and in order to sound natural.
Note: This is not an ancient Chinese phrase by any means. It's just that we received a lot of requests for this phrase.
This is as close as you can get to the phrase “trust no man,” though technically, no gender is specified.
Trust No One / Trust No Man
誰も信じるな is as close as you can get to the phrase “trust no man” in Japanese, though no gender is specified.
The first two characters mean everyone or anyone but change to “no one” with the addition of a negative verb.
The third through fifth characters express the idea of believing in, placing trust in, confiding in, or having faith in.
The last character makes the sentence negative (without the last character, this would mean “trust everyone,” with that last character, it's “trust no one”).
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Truth Flashed Through The Mind
Tsuki no Kokoro / Mind like the Moon
There is one single thread binding my Way together
吾道一以貫之 is a phrase from the Analects of Confucius that translates as “My Way has one thread that runs through it.”
Other translations include:
My Way is penetrated by a single thread.
There is one single thread binding my Way together.
My Way is run through with a unifying thread.
My Way is Consistent.
And sometimes poetic license is taken, and it is translated as:
My Way is the only one; I'll treasure it and stick to it with humility until the end.
After this was said, some 2500+ years ago, another disciple of Confucius clarified the meaning by stating, “Our master's Way is to be loyal and have a sense of reciprocity.”
In Japanese, this is purported to be romanized as “Waga michi ichi wo motte kore wo tsuranuku,” though some will argue the true pronunciation.
Note: Sometimes written 吾道以一貫之 instead of 吾道一以貫之 with no difference in meaning.
A Wise Man Changes His Mind (but a fool never will)
君子豹変す is a Japanese proverb that suggests that a wise man is willing to change his mind, but a fool will stubbornly never change his.
The first word is 君子 (kunshi), a man of virtue, a person of high rank, a wise man.
The second word is 豹変 (hyouhen), sudden change, complete change.
The last part, す (su), modifies the verb to a more humble form.
The “fool” part is merely implied or understood. So if wise and noble people are willing to change their minds, it automatically says that foolish people are unwilling to change.
Work Together with One Mind
Work Together with One Heart
Solidarity / Working Together as One
Alert / On Guard / Lingering Mind
Zanshin
残心 is a Japanese Kanji word meaning: continued alertness; unrelaxed alertness; remaining on one's guard; lingering mind, and being prepared for a counterstrike. This context is used in martial arts, which is probably why you are looking up this word.
In archery and golf, it can be the follow-through.
In the context of love and relationships, it can be lingering affection, attachment, regret, regrets, or reluctance.
Zen Heart / Zen Mind
禪心 represents an image of your meditation coming from and filling your heart.
The meaning of the first character is “meditation” and the second character is usually defined as “heart” or sometimes “mind.”
There is a two-fold meaning here, as a good meditation session must start with a centered heart or mind. Yet at the same time, meditation serves to cleanse, focus, and center the heart and mind.
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Gallery Price: $106.00
Your Price: $58.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $202.00
Your Price: $111.88
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $118.88
Gallery Price: $200.00
Your Price: $118.88
Gallery Price: $202.00
Your Price: $111.88
Gallery Price: $108.00
Your Price: $59.88
Gallery Price: $198.00
Your Price: $109.88
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Sword | 劍 剑 | ken / tsurugi | jiàn / jian4 / jian | chien |
| Sword | 剱 剣 | ken | jiàn / jian4 / jian | chien |
| One Day Seems Like 1000 Years | 一日千秋 | ichi jitsu sen shuu ichijitsusenshuu ichi jitsu sen shu | yí rì qiān qiū yi2 ri4 qian1 qiu1 yi ri qian qiu yiriqianqiu | i jih ch`ien ch`iu ijihchienchiu i jih chien chiu |
| Ace One | 幺 | yao | yāo / yao1 / yao | |
| Beautiful Heart Beautiful Mind | 美しい心 | utsukushii kokoro utsukushiikokoro utsukushi kokoro | ||
| Beautiful Mind | 美麗心靈 美丽心灵 | měi lì xīn líng mei3 li4 xin1 ling2 mei li xin ling meilixinling | mei li hsin ling meilihsinling |
|
| Mind of the Beginner | 初心 | sho shin / shoshin | chū xīn / chu1 xin1 / chu xin / chuxin | ch`u hsin / chuhsin / chu hsin |
| Best Number One | 一番 | ichi ban / ichiban | ||
| Bodhicitta: Enlightened Mind | 冒地質多 冒地质多 | boujiishitta bojishitta | mào dì zhì duō mao4 di4 zhi4 duo1 mao di zhi duo maodizhiduo | mao ti chih to maotichihto |
| The Bodhi Mind | 菩提心 | bo dai shin bodaishin | pú tí xīn pu2 ti2 xin1 pu ti xin putixin | p`u t`i hsin putihsin pu ti hsin |
| Body and Mind | 身心 | shin jin / shinjin | shēn xīn / shen1 xin1 / shen xin / shenxin | shen hsin / shenhsin |
| Body Mind Spirit | 身心霊 | mi shin rei mishinrei | ||
| Buddha Heart Mind of Buddha | 佛心 | busshin / bushin | fó xīn / fo2 xin1 / fo xin / foxin | fo hsin / fohsin |
| Seeing one’s Nature and becoming a Buddha | 見性成佛 见性成佛 | ken shou jou butsu kenshoujoubutsu ken sho jo butsu | jiàn xìng chéng fó jian4 xing4 cheng2 fo2 jian xing cheng fo jianxingchengfo | chien hsing ch`eng fo chienhsingchengfo chien hsing cheng fo |
| Calm and Open Mind | 虛心 虚心 | ko shin / koshin | xū xīn / xu1 xin1 / xu xin / xuxin | hsü hsin / hsühsin |
| Mark the boat to find the lost sword Ignoring the changing circumstances of the world | 刻舟求劍 刻舟求剑 | kokushuukyuuken kokushukyuken | kè zhōu qiú jiàn ke4 zhou1 qiu2 jian4 ke zhou qiu jian kezhouqiujian | k`o chou ch`iu chien kochouchiuchien ko chou chiu chien |
| Working Together as One Cooperation | 同心協力 同心协力 | tóng xīn xié lì tong2 xin1 xie2 li4 tong xin xie li tongxinxieli | t`ung hsin hsieh li tunghsinhsiehli tung hsin hsieh li |
|
| Drinking the water of a well: One should never forget who dug it | 吃水不忘掘井人 | chī shuǐ bú wàng jué jǐng rén chi1 shui3 bu2 wang4 jue2 jing3 ren2 chi shui bu wang jue jing ren chishuibuwangjuejingren | ch`ih shui pu wang chüeh ching jen chih shui pu wang chüeh ching jen |
|
| The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet | 別人屁臭自家香 别人屁臭自家香 | bié rén pì chòu zì jiā xiāng bie2 ren2 pi4 chou4 zi4 jia1 xiang1 bie ren pi chou zi jia xiang bierenpichouzijiaxiang | pieh jen p`i ch`ou tzu chia hsiang pieh jen pi chou tzu chia hsiang |
|
| The one who retreats 50 paces mocks the one to retreats 100 | 五十步笑百步 | wù shí bù xiào bǎi bù wu4 shi2 bu4 xiao4 bai3 bu4 wu shi bu xiao bai bu wushibuxiaobaibu | wu shih pu hsiao pai pu wushihpuhsiaopaipu |
|
| One Good Deed Each Day | 一日一善 | ichi nichi ichi zen ichinichiichizen | yī rì yī shàn yi1 ri4 yi1 shan4 yi ri yi shan yiriyishan | i jih i shan ijihishan |
| Heart Mind Spirit | 心 | kokoro | xīn / xin1 / xin | hsin |
| Words Have Enormous Weight: One Word Worth Nine Caldrons | 一言九鼎 | yī yán jiǔ dǐng yi1 yan2 jiu3 ding3 yi yan jiu ding yiyanjiuding | i yen chiu ting iyenchiuting |
|
| Heijoshin Presence of Mind | 平常心 | hei jou shin heijoushin hei jo shin | píng cháng xīn ping2 chang2 xin1 ping chang xin pingchangxin | p`ing ch`ang hsin pingchanghsin ping chang hsin |
| Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot | 百尺竿頭更進一步 百尺竿头更进一步 | bǎi chǐ gān tóu gèng jìng yī bù bai3 chi3 gan1 tou2 geng4 jing4 yi1 bu4 bai chi gan tou geng jing yi bu baichigantougengjingyibu | pai ch`ih kan t`ou keng ching i pu pai chih kan tou keng ching i pu |
|
| Immovable Mind | 不動心 | fu dou shin fudoushin fu do shin | ||
| Seeking Mind | 尋求心 寻求心 | jingu shin / jingushin | xún qiú xīn xun2 qiu2 xin1 xun qiu xin xunqiuxin | hsün ch`iu hsin hsünchiuhsin hsün chiu hsin |
| One Justice Can Overpower 100 Evils | 一正壓百邪 一正压百邪 | yī zhèng yā bǎi xié yi1 zheng4 ya1 bai3 xie2 yi zheng ya bai xie yizhengyabaixie | i cheng ya pai hsieh ichengyapaihsieh |
|
| The Nature of Enlightenment in One's Mind | 覺性 觉性 | kakushou / kakusho | jué xìng / jue2 xing4 / jue xing / juexing | chüeh hsing / chüehhsing |
| Life-Saving Sword | 活人剣 | katsu jin ken katsujinken | ||
| Kendo The Way of the Sword | 剱道 / 劍道 剣道 | kendou / kendo | jiàn dào / jian4 dao4 / jian dao / jiandao | chien tao / chientao |
| Resolute Mind | 決定心 决定心 | ketsujou shin ketsujoushin ketsujo shin | jué dìng xīn jue2 ding4 xin1 jue ding xin juedingxin | chüeh ting hsin chüehtinghsin |
| To Know Hardship, One Must Experience It | 不當和尚不知頭冷 不当和尚不知头冷 | bù dāng hé shàng bù zhī tóu lěng bu4 dang1 he2 shang4 bu4 zhi1 tou2 leng3 bu dang he shang bu zhi tou leng | pu tang ho shang pu chih t`ou leng pu tang ho shang pu chih tou leng |
|
| We are not born with knowledge, how does one achieve maturity? | 人非生而知之者熟能無惑 | rén fēi shēng ér zhī zhī zhě shú néng wú huò ren2 fei1 sheng1 er2 zhi1 zhi1 zhe3 shu2 neng2 wu2 huo4 ren fei sheng er zhi zhi zhe shu neng wu huo | jen fei sheng erh chih chih che shu neng wu huo | |
| Lingering Mind | 殘心 残心 | zan shin / zanshin | cán xīn / can2 xin1 / can xin / canxin | ts`an hsin / tsanhsin / tsan hsin |
| Listen with Open Mind | 虛己以聽 虚己以听 | xū jǐ yǐ tīng xu1 ji3 yi3 ting1 xu ji yi ting xujiyiting | hsü chi i t`ing hsüchiiting hsü chi i ting |
|
| Listen to Both Sides and be Enlightened, Listen to One Side and be in the Dark | 兼聽則明偏聽則暗 兼听则明偏听则暗 | jiān tīng zé míng, piān tīng zé àn jian1 ting1 ze2 ming2, pian1 ting1 ze2 an4 jian ting ze ming, pian ting ze an | chien t`ing tse ming, p`ien t`ing tse an chien ting tse ming, pien ting tse an |
|
| Live By The Sword Die By The Sword | 凡動刀的必死在刀下 凡动刀的必死在刀下 | fán dòng dāo de bì sǐ zài dāo xià fan2 dong4 dao1 de bi4 si3 zai4 dao1 xia4 fan dong dao de bi si zai dao xia | fan tung tao te pi ssu tsai tao hsia | |
| Loving Heart One’s Love | 戀心 恋心 | koi gokoro / koigokoro | ||
| Be Master of Mind, Not Mastered by Mind | 願作心師不師於心 愿作心师不师于心 | yuàn zuò xīn shī bù shī yú xīn yuan4 zuo4 xin1 shi1 bu4 shi1 yu2 xin1 yuan zuo xin shi bu shi yu xin yuanzuoxinshibushiyuxin | yüan tso hsin shih pu shih yü hsin | |
| Merciful Heart The Light from a Buddha Mind | 心光 | shin kou / shinkou / shin ko | xīn guāng xin1 guang1 xin guang xinguang | hsin kuang hsinkuang |
| Mind Body Spirit | 身心靈 / 身心霊 身心灵 | mi shin rei mishinrei | shēn xīn líng shen1 xin1 ling2 shen xin ling shenxinling | shen hsin ling shenhsinling |
| Mind Over Matter | 心勝於物 心胜于物 | xīn shèng yú wù xin1 sheng4 yu2 wu4 xin sheng yu wu xinshengyuwu | hsin sheng yü wu hsinshengyüwu |
|
| Mind Over Matter | 物質性を超越する精神力 | busshitsu-sei o chouetsu suru seishin-ryoku bushitsu-sei o choetsu suru seishin-ryoku | ||
| Energy Sword Body in Concert | 気剣体一致 / 氣劍體一致 气剑体一致 | ki ken tai icchi kikentaiicchi ki ken tai ichi | ||
| Mind Your Own Business | 不干己事不張口一問搖頭三不知 不干己事不张口一问摇头三不知 | bù gān jǐ shì bù zhāng kǒu yī wèn yáo tóu sān bù zhī bu4 gan1 ji3 shi4 bu4 zhang1 kou3 yi1 wen4 yao2 tou2 san1 bu4 zhi1 bu gan ji shi bu zhang kou yi wen yao tou san bu zhi | pu kan chi shih pu chang k`ou i wen yao t`ou san pu chih pu kan chi shih pu chang kou i wen yao tou san pu chih |
|
| Mind Your Own Business | 余計なお世話 | yokei na osewa yokeinaosewa | ||
| Mind’s Eye | 心眼 | shingan | xīn yǎn / xin1 yan3 / xin yan / xinyan | hsin yen / hsinyen |
| Mind Like Water | 水の心 | mizu no kokoro mizunokokoro | ||
| Morality of Mind | 心德 | xīn dé / xin1 de2 / xin de / xinde | hsin te / hsinte | |
| No Mind Mushin | 無心 无心 | mu shin / mushin | wú xīn / wu2 xin1 / wu xin / wuxin | wu hsin / wuhsin |
| No one knows a son better than the father | 知子莫若父 | zhī zǐ mò ruò fù zhi1 zi3 mo4 ruo4 fu4 zhi zi mo ruo fu zhizimoruofu | chih tzu mo jo fu chihtzumojofu |
|
| One Direction | 一世代 | yí shì dài yi1 shi4 dai4 yi shi dai yishidai | i shih tai ishihtai |
|
| One Direction | ワンダイレクション | wan dairekushon wandairekushon | ||
| One Family Under Heaven | 天下一家 | tenka ikka / tenkaikka / tenka ika | tiān xià yī jiā tian1 xia4 yi1 jia1 tian xia yi jia tianxiayijia | t`ien hsia i chia tienhsiaichia tien hsia i chia |
| One Heart One Mind Heart and Soul | 一心 | isshin / ishin | yī shì dài yi1 shi4 dai4 yi shi dai yishidai | i shih tai ishihtai |
| One Key Opens One Lock | 一把鑰匙開一把鎖 一把钥匙开一把锁 | yī bǎ yào shi kāi yī bǎ suǒ yi1 ba3 yao4 shi5 kai1 yi1 ba3 suo3 yi ba yao shi kai yi ba suo yibayaoshikaiyibasuo | i pa yao shih k`ai i pa so ipayaoshihkaiipaso i pa yao shih kai i pa so |
|
| One Love | 一份愛 一份爱 | yí fèn ài yi2 fen4 ai4 yi fen ai yifenai | i fen ai ifenai |
|
| One Love | 一つの愛 | hito tsu no ai hitotsunoai | ||
| One Mind Unity | 和合 | wagou / wago wago / wago | hé hé / he2 he2 / he he / hehe | ho ho / hoho |
| One who walks by the river may end up with wet feet | 常在河邊走哪能不濕鞋 常在河边走哪能不湿鞋 | cháng zài hé biān zǒu nǎ néng bù shī xié chang2 zai4 he2 bian1 zou3 na3 neng2 bu4 shi1 xie2 chang zai he bian zou na neng bu shi xie | ch`ang tsai ho pien tsou na neng pu shih hsieh chang tsai ho pien tsou na neng pu shih hsieh |
|
| One | 一 | ichi | yī / yi1 / yi | i |
| Open and Calm Mind | 虛心坦懐 虚心坦懐 | kyo shin tan kai kyoshintankai | ||
| Open Mind | 開覺 开觉 | kaikaku / kaikaku | kāi jué / kai1 jue2 / kai jue / kaijue | k`ai chüeh / kaichüeh / kai chüeh |
| An Open Book Benefits Your Mind | 開卷有益 开卷有益 | kāi juàn yǒu yì kai1 juan4 you3 yi4 kai juan you yi kaijuanyouyi | k`ai chüan yu i kaichüanyui kai chüan yu i |
|
| The Original Mind | 本心 | hon shin / honshin | běn xīn / ben3 xin1 / ben xin / benxin | pen hsin / penhsin |
| Patience Brings Peace of Mind | 忍耐は心の平和をもたらす | nintai wa kokoro no heiwa o motarasu | ||
| Patience Yields Peace of Mind | 能忍自安 | néng rěn zì ān neng2 ren3 zi4 an1 neng ren zi an nengrenzian | neng jen tzu an nengjentzuan |
|
| Peace of Mind | 內心的寧靜 内心的宁静 | nèi xīn de níng jìng nei4 xin1 de ning2 jing4 nei xin de ning jing neixindeningjing | nei hsin te ning ching neihsinteningching |
|
| Peace of Mind | 和平 | wa hei / wahei | hé píng / he2 ping2 / he ping / heping | ho p`ing / hoping / ho ping |
| Peaceful Heart Peace of Mind Calm Mind | 安心 | an shin / anshin | ān xīn / an1 xin1 / an xin / anxin | an hsin / anhsin |
| Perfectly Sincere Mind | 至誠心 至诚心 | shi jou shin shijoushin shi jo shin | zhì chéng xīn zhi4 cheng2 xin1 zhi cheng xin zhichengxin | chih ch`eng hsin chihchenghsin chih cheng hsin |
| Presence of Mind | 泰然自若 | taizenjijaku | tài rán zì ruò tai4 ran2 zi4 ruo4 tai ran zi ruo tairanziruo | t`ai jan tzu jo taijantzujo tai jan tzu jo |
| Presence of Mind | 落着き | ochitsuki | ||
| Prideful Mind Self-Respecting Heart | 自尊心 | ji son shin jisonshin | zì zūn xīn zi4 zun1 xin1 zi zun xin zizunxin | tzu tsun hsin tzutsunhsin |
| Proud Of One’s Name | 行不更名坐不改姓 | xíng bù gēng míng zuò bù gǎi xìng xing2 bu4 geng1 ming2 zuo4 bu4 gai3 xing4 xing bu geng ming zuo bu gai xing | hsing pu keng ming tso pu kai hsing | |
| Purity of Mind | 心澄淨 | shin chou jou shinchoujou shin cho jo | xīn chéng jìng xin1 cheng2 jing4 xin cheng jing xinchengjing | hsin ch`eng ching hsinchengching hsin cheng ching |
| One Who Does Not Do Bad Things, Worries Not of Knocks at His Door | 白天不做虧心事夜半敲門不吃驚 白天不做亏心事夜半敲门不吃惊 | bái tiān bú zuò kuī xīn shì yè bàn qiāo mén bù chī jīng bai2 tian1 bu2 zuo4 kui1 xin1 shi4 ye4 ban4 qiao1 men2 bu4 chi1 jing1 bai tian bu zuo kui xin shi ye ban qiao men bu chi jing | pai t`ien pu tso k`uei hsin shih yeh pan ch`iao men pu ch`ih ching pai tien pu tso kuei hsin shih yeh pan chiao men pu chih ching |
|
| One who is drenched in rain does not fear drops of dew | 被雨淋過的人不怕露水 被雨淋过的人不怕露水 | bèi yǔ lín guò de rén bù pà lù shuǐ bei4 yu3 lin2 guo4 de ren2 bu4 pa4 lu4 shui3 bei yu lin guo de ren bu pa lu shui | pei yü lin kuo te jen pu p`a lu shui pei yü lin kuo te jen pu pa lu shui |
|
| Sword of Death | 殺人剣 杀人剣 | satsu jin ken satsujinken | ||
| Stable - Mind at Peace | 安穩 安稳 | an non / annon | ān wěn / an1 wen3 / an wen / anwen | |
| Strong Mind Strong Body | 強壯的身體堅強的心態 强壮的身体坚强的心态 | qiáng zhuàng de shēn tǐ jiān qiáng de xīn tài qiang2 zhuang4 de shen1 ti3 jian1 qiang2 de xin1 tai4 qiang zhuang de shen ti jian qiang de xin tai | ch`iang chuang te shen t`i chien ch`iang te hsin t`ai chiang chuang te shen ti chien chiang te hsin tai |
|
| Strong Body, Strong Mind | 強い體強い心 強い体強い心 | tsuyo i karada tsuyo i kokoro tsuyoikaradatsuyoikokoro | ||
| The Strong One | 強いもの | tsuyoi mono tsuyoimono | ||
| Sword Saint | 剣聖 / 剣聖 剣圣 | kensei | jiàn shèng jian4 sheng4 jian sheng jiansheng | chien sheng chiensheng |
| The Chosen One | 選ばれし者 | erabareshimono | ||
| A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One | 千里も一里 | sen ri mo ichi ri senrimoichiri | ||
| When Three People Gather, One Becomes a Teacher | 三人行必有我師 三人行必有我师 | sān rén xíng bì yǒu wǒ shī san1 ren2 xing2 bi4 you3 wo3 shi1 san ren xing bi you wo shi sanrenxingbiyouwoshi | san jen hsing pi yu wo shih sanjenhsingpiyuwoshih |
|
| Time Waits For No One | 歳月人を待たず | sai getsu hito o ma ta zu saigetsuhitoomatazu | ||
| Trust No One Trust No Man | 無法信任 无法信任 | wú fǎ xìn rèn wu2 fa3 xin4 ren4 wu fa xin ren wufaxinren | wu fa hsin jen wufahsinjen |
|
| Trust No One Trust No Man | 誰も信じるな | dare mo shin ji ru na daremoshinjiruna | ||
| Truth Flashed Through The Mind | 參悟 参悟 | cān wù / can1 wu4 / can wu / canwu | ts`an wu / tsanwu / tsan wu | |
| Tsuki no Kokoro Mind like the Moon | 月の心 | tsuki no kokoro tsukinokokoro | ||
| There is one single thread binding my Way together | 吾道一以貫之 吾道一以贯之 | ware dou tsurayuki waredoutsurayuki ware do tsurayuki | wú dào yī yǐ guàn zhī wu2 dao4 yi1 yi3 guan4 zhi1 wu dao yi yi guan zhi wudaoyiyiguanzhi | wu tao i i kuan chih wutaoiikuanchih |
| A Wise Man Changes His Mind (but a fool never will) | 君子豹変す | kun shi hyou hen su kunshihyouhensu kun shi hyo hen su | ||
| Work Together with One Mind | 一味同心 | ichi mi dou shin ichimidoushin ichi mi do shin | ||
| Work Together with One Heart | 齊心協力 齐心协力 | qí xīn xié lì qi2 xin1 xie2 li4 qi xin xie li qixinxieli | ch`i hsin hsieh li chihsinhsiehli chi hsin hsieh li |
|
| Solidarity Working Together as One | 一致団結 | icchidanketsu ichidanketsu | ||
| Alert On Guard Lingering Mind | 残心 | zan shin / zanshin | ||
| Zen Heart Zen Mind | 禪心 禅心 | zen shin / zenshin | chán xīn / chan2 xin1 / chan xin / chanxin | ch`an hsin / chanhsin / chan hsin |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...



















































































































